Ranked 1 Proven Hyperpigmentation Treatment Options & Melasma Treatment Options: What Really Works?
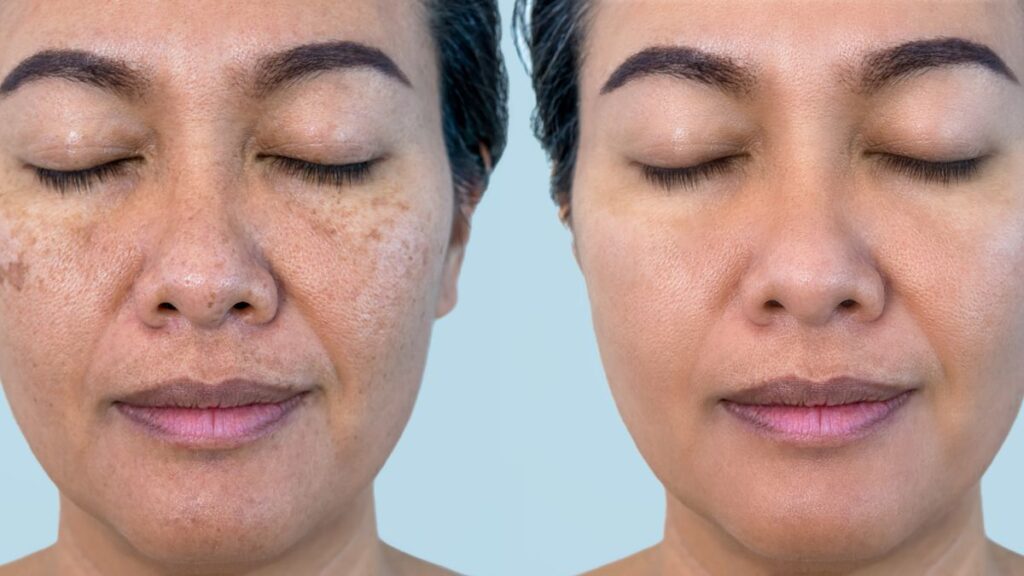
Hyperpigmentation and melasma are among the most challenging skin concerns in aesthetic and dermatology practice. Dark patches, uneven skin tone, and recurring pigmentation can significantly affect patient confidence, especially when results from topical products are inconsistent or short-lived.
Understanding the different hyperpigmentation treatment options available is key to effectively addressing skin concerns.
This article explores what truly works for hyperpigmentation and melasma, comparing treatment options from topical care to advanced energy-based devices, with a focus on long-term skin tone improvement.
Understanding Hyperpigmentation and Melasma
Hyperpigmentation occurs when excess melanin is produced in certain areas of the skin, leading to dark spots or patches. Common triggers include sun exposure, acne inflammation, hormonal changes, and aging.
For individuals seeking relief, exploring hyperpigmentation treatment options can lead to tailored solutions based on skin type and concerns.
Melasma is a chronic form of hyperpigmentation, often symmetrical, typically appearing on the cheeks, forehead, upper lip, and chin. It is strongly associated with:
- Hormonal fluctuations (pregnancy, oral contraceptives)
- UV and heat exposure
- Genetic predisposition
Because melasma involves deeper pigment and vascular components, it is more difficult to treat and has a higher recurrence rate.
Topical Treatments: First-Line but Limited
Topical skincare is usually the first step for pigmentation removal treatment management.
Common ingredients include:
- Hydroquinone – inhibits melanin production (short-term use)
- Retinoids – accelerate cell turnover
- Vitamin C – antioxidant and brightening agent
- Azelaic acid & kojic acid – reduce pigment formation
Exploring Hyperpigmentation Treatment Options
While topical treatments can improve mild pigmentation, they often provide slow results and limited effectiveness for deep or persistent melasma.
Chemical Peels for Pigmentation Control

Chemical peels such as glycolic acid, salicylic acid, and TCA peels exfoliate the epidermis and help remove superficial pigment.
Pros:
- Improves skin brightness
- Enhances penetration of topical agents
Cons:
- Limited effect on dermal melasma
- Risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), especially in darker skin types
Peels are best used as adjunct treatments, not standalone solutions for melasma.
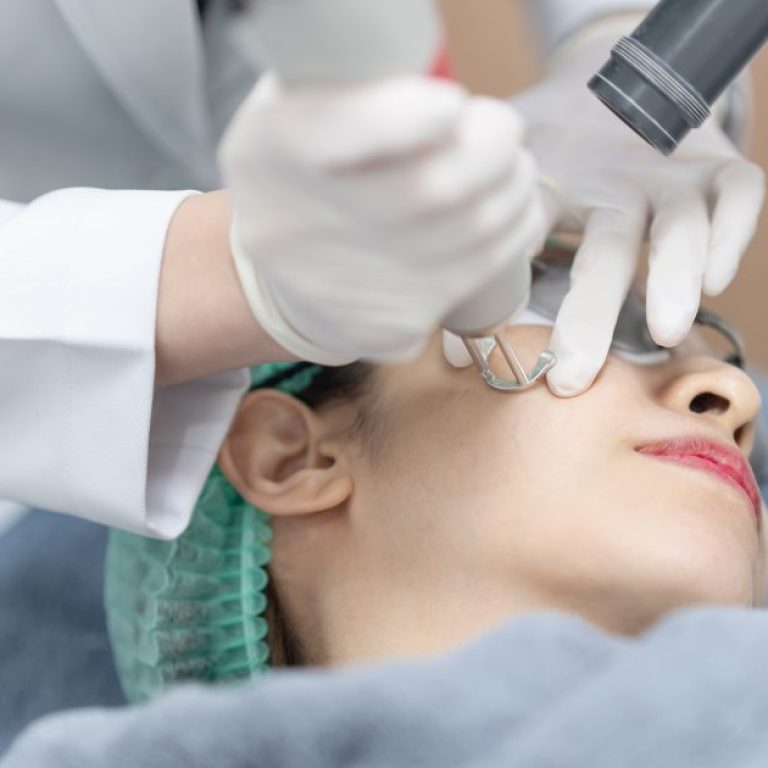
Laser and Energy-Based Treatment Options
Advanced laser technologies have transformed pigmentation treatment by targeting melanin more precisely while preserving surrounding tissue.
1. Picosecond & Q-Switched Lasers
- Break down pigment particles through photoacoustic effects
- Effective for freckles, sunspots, and superficial pigmentation
- Require multiple sessions for melasma
2. Fractional Non-Ablative Lasers (1550nm / 1927nm)
- Stimulate skin renewal and pigment dispersion
- Improve overall skin tone and texture
- Lower risk of PIH compared to aggressive resurfacing
3. Fractional CO2 Laser (Cautious Use)
- Improves texture and pigment irregularities
- Best for combined concerns (scars + pigmentation)
- Requires strict patient selection and post-care
Energy-based treatments are most effective when combined with topical therapy and sun protection.
Role of IPL in Pigmentation Treatment
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) targets melanin and hemoglobin, making it suitable for mixed pigmentation and redness.
- Works best for sun-induced pigmentation
- Less effective for hormonal melasma
- Requires multiple low-energy sessions
IPL is often used as a maintenance treatment rather than a primary melasma solution.
The Importance of Sun Protection and Maintenance
Regardless of treatment type, strict sun protection is essential.
Key recommendations:
- Broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 30–50+)
- Physical blockers (zinc oxide, titanium dioxide)
- Avoid heat exposure and aggressive skincare
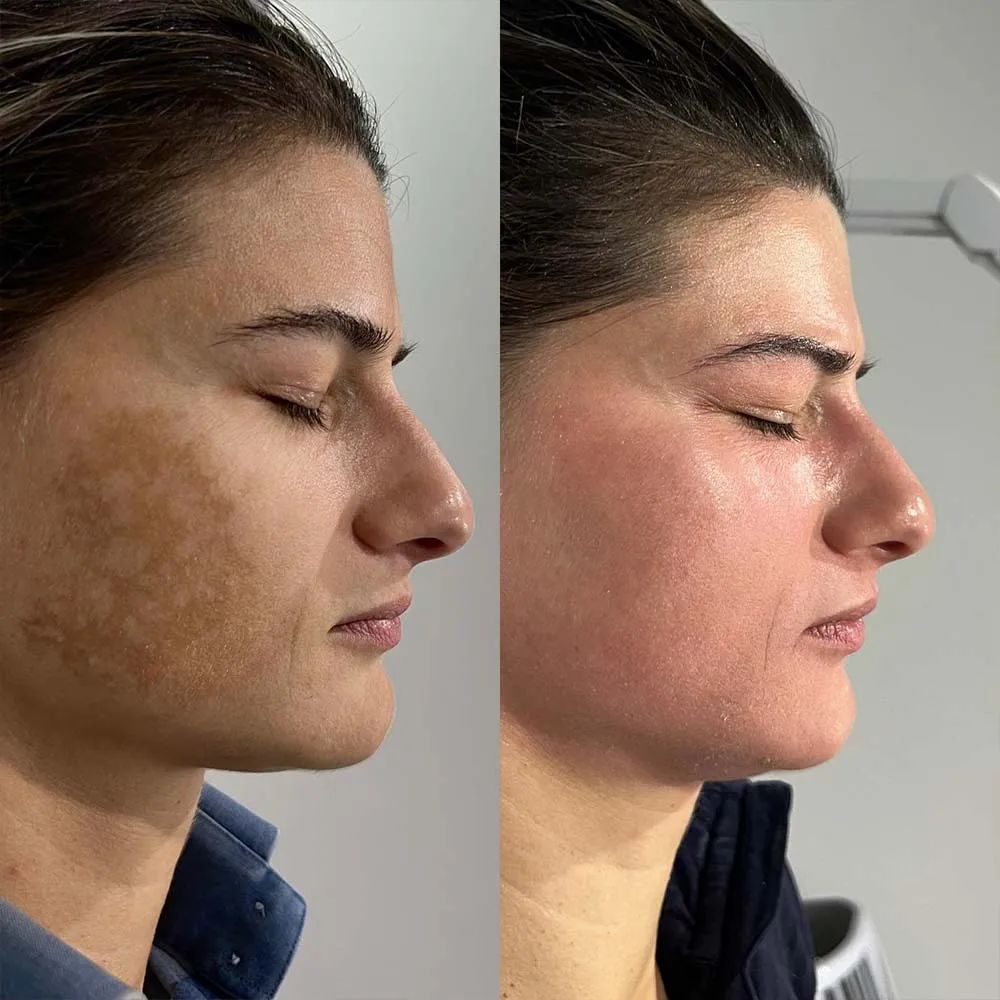
Without maintenance, melasma recurrence is common—even after successful laser treatment for melasma.
What Really Works for Melasma?
Clinical experience shows that the most effective approach is combination therapy, including:
- Gentle laser or energy-based treatments
- Medical-grade topical products
- Long-term sun protection and lifestyle management
Rather than aggressive single treatments, controlled, repeated stimulation delivers safer and more sustainable results.
Conclusion
Hyperpigmentation and melasma require a strategic, long-term treatment plan. While topical agents and peels play supportive roles, advanced laser technologies—used correctly—offer superior control of pigmentation and skin tone improvement.
For aesthetic clinics and device providers, offering customizable, multi-modality solutions is key to achieving consistent patient satisfaction. Educating patients about realistic expectations, gradual improvement, and long-term maintenance is equally important for reducing recurrence and building treatment trust.
At last, if you want to learn more about Laser Freckle Removal, pls kindly refer to,
👉How long does professional laser freckle removal take to work?


2 thoughts on “Hyperpigmentation & Melasma Treatment Options: What Works?”